|
|
|
CLICK BUTTON TO GO TO |
|
|
|
|
|
|
JewishWikipedia.info
See our new site:
|
T O P I C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Summary
__________________________________
Islamic–Jewish relations started in the 7th century AD with the origin and spread of Islam in the Arabian peninsula. The two religions share similar values, guidelines, and principles. Islam also incorporates Jewish history as a part of its own. Muslims regard the Children of Israel as an important religious concept in Islam. Moses, the most important prophet of Judaism, is also considered a prophet and messenger in Islam. Moses is mentioned more in the Quran than any other individual, and his life is narrated and recounted more than that of any other prophet. There are approximately forty-three references to the Israelites in the Quran (excluding individual prophets), and many in the Hadith. Later rabbinic authorities and Jewish scholars such as Maimonides discussed the relationship between Islam and Jewish law. Maimonides himself, it has been argued, was influenced by Islamic legal thought.
Because Islam and Judaism share a common origin in the Middle East through Abraham, both are considered Abrahamic religions. There are many shared aspects between Judaism and Islam; Islam was strongly influenced by Judaism in its fundamental religious outlook, structure, jurisprudence and practice. Because of this similarity, as well as through the influence of Muslim culture and philosophy on the Jewish community within the Islamic world, there has been considerable and continued physical, theological, and political overlap between the two faiths in the subsequent 1,400 years. Notably, the first Islamic Waqf (an inalienable religious endowment in Islamic law) was donated by a Jew, Rabbi Mukhayriq. And in 1027, a Jew, Samuel ibn Naghrillah became top advisor and military general of the Taifa of Granada.
Mohammed dreamed of uniting the dissident, warring Arab tribes into one people, giving them a unifying religion. He claimed that God had manifested Himself to him in the form of the angel Gabriel.
The Quran, Qur'an or Koran literally meaning "the recitation" is the central religious text of Islam, which Muslims believe to be a revelation from God. It is widely regarded by Muslims as the finest piece of literature in the Arabic language .
Muslims believe the Quran was verbally revealed by God to Muhammad through the angel Gabriel over approximately 23 years, beginning on 22 December 609 CE, when Muhammad was 40, and concluding in 632, the year of his death. It is regarded as a proof of his prophethood.
In the sixth century the Arabs were desert nomads, in the seventh century they were conquerors on the march, in the eighth century they were masters of an empire that made the Mediterranean a Mohammedan lake, and in the ninth century they were the standard-bearers of a dazzling civilization. leaders in art. architecture, and science, while Western Europe was sinking deeper and deeper into a dark morass of its own making. Damascus fell to them in 635. Palestine in 638, Syria in 640. Egypt in 641 and the Sassanid Empire in 636.
In 711 a mixed force of Arabs and Berbers invaded Spain and by 715 had crossed the Pyrenees. They were stopped by the French at the Battle of Chalons in 732. This battle resulted in a power stalemate for Mohammedans and Christians. The spread of Mohammedanism was checked in the East by the Byzantine Empire and in the West by France, the spread of Christianity into Africa and Asia was checked by the counterforce of Mohammedanism.
Soon after the death of Mohammed, the hostility against the Jews, manufactured out of political expediency, vanished. While legislation against non-Mohammedans existed was often ignored the Jews were never secure as changes in the political or social climate often lead to persecution, violence and death. For example in 1066, the Jewish Vizier of Granada, Spain, was crucified by an Arab mob who then razed the Jewish quarter and slaughtered its 5,000 inhabitants. The riot was incited by Muslim preachers who claimed that the Jews had inordinate political power.
The span of the Jewish Golden Age in the Mohammedan civilization corresponded to the life span of the Islamic Empire. When this broke up. the Jewish Golden Age broke up. In 1453 Byzantium fell to the Turks so heralding the Ottoman Empire. In Europe the Crusades saw many leaving farming and settling in cities so starting the Reformation. In 1492, the Jews were expelled from Spain with many settling in the Ottoman Empire, Persia/Iran and North African countries.
A low point was reached in Arab countries during the 19th century when Jews in most of North Africa (including Algeria, Tunisia, Egypt, Libya and Morocco) were forced to live in ghettos. In Morocco, which had the largest Jewish community in the Islamic Diaspora, they had to walk barefoot or wear straw shoes when outside the ghetto. The British Vice Consul in Mosul, wrote in 1909:
The attitude of the Muslims toward the Christians and the Jews is that of a master towards slaves, whom he treats with a certain lordly tolerance so long as they keep their place. Any sign of pretension to equality is promptly repressed.
(Note: This developed during a period during which Christian attitude to Jews was often repressive including the Inquisition, pogroms, expulsions and extra taxes)
In 1916 the British-French Sykes-Picot agreement split the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East between them with the British occupying the southern half and the French the Northern half. The British were given the protectorate of Palestine by the League of Nations after World War1. 80% was given to the Arabs and became Transjordan. They received full sovereignty in 1946 and changed their name to Jordan.
The British mandate was marked by the growth of Jewish and Arab nationalism and led to the Peel Report of 1937 splitting the country between them. This was rejected by the Arabs.
The United Nations split Palestine between The Jews and Arabs. Israel came into existence in 1948 and was invaded by the surrounding Arab countries after they had all rejected the partition agreement. Go to Israel for more information
In December 1949 following the Israel War of Independence the Arab League would not resettle refugees so they would act as a problem for Israel. The UN set up a refugee agency called UNRWA to assist Arab refugees.
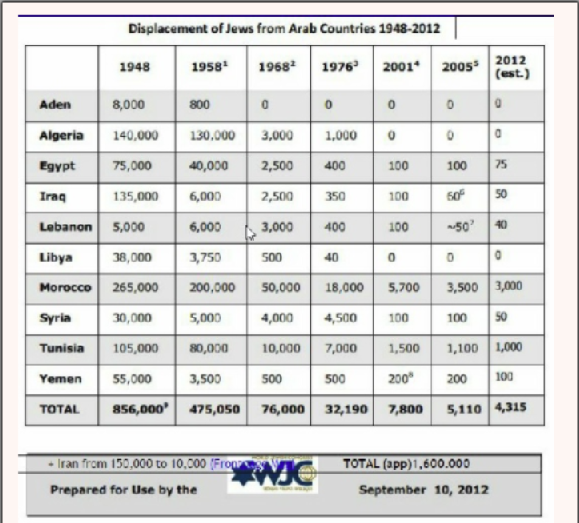
The number of Jews in Arab countries fell from 1,600,000 (app) in 1948 to 4,315 (est) in 2012 (see Expulsion of the Jews from Arab countries, 1948-2012.)
Today animosity is directed towards Israel and against worldwide Jews in the form of anti-Semitism.
Click for details of relationships between them.
Egypt and Jordan have signed peace agreements with Israel since it was established in 1948.
MUSLIM-JEWISH RELATIONS - SUMMARY
Religion, Oxford Research Encyclopedias
Muslim-Jewish relations began with the emergence of Islam in 7th-century Arabia, but contacts between pre-Jewish Israelites and pre-Muslim Arabs had been common for nearly two millennia previously. These interactions inform the earliest relations between Muslims and Jews and serve as precursors to the social, cultural, religious, political, and institutional relations between Muslims and Jews from the 7th century to the present. Areas and periods of particular importance are 7th-century Arabia with first contacts between Jews and the earliest Muslims, 8th–9th-century Middle East with the establishment of legal and social status of Jews in Islam, the 9th to 14th centuries in many parts of the Muslim world with the development of great Jewish intellectual advances under Islamic influence, the subsequent decline of the Muslim world and its negative impact on Jews and other minorities, the period under colonial powers with the rise of national movements and the subsequent transition to independent nation-states that includes the rise of both Jewish and Palestinian nationalisms, and the current status of Muslim-Jewish relations today. Common issues include language production; cultural production including literature, hermeneutics, and systematic thinking; legal developments, political relations, religious commonalities and differences, and economic relations and partnerships.
THE
INCREDIBLE
STORY OF THE JEWISH PEOPLE

ISLAM, JUDAISM, BELIEFS AND HISTORY
